


The Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines logic as follows: a science that deals with the principles and criteria of inference and demonstration: the science of the formal principles of reasoning
mathematics is the science of abstract structures and patterns, constructed out of different statements, which need to be proven true

... remarkable counting abilities, such as Shakuntala Devi: she was able to multiply two 13 digit numbers in 28 seconds in 1980
... intuitive understanding, such as Srinivasa Ramanujan: he wrote down nearly 3.900 new results (theorems, identities and equations)
... insight into abstract structures, such as Alexander Grothendiek: he worked on a rebuilding of algebraic geometry

Agricultural Societies
Ancient Egypt
Mesopotamia/Babylon
Ancient China
Ancient India
calendar
religion: Nile river god Hapi
measuring device
landmeasure
measure unit
legth and area calculation
decimal system
binary counting system
fractions
Eye of Horus: geometric theory
accurate value of pi
Pyramid - the golden ratio, right angle

Pythagoras
right-angled triangles
the harmonic serie
Euclid
300BC "The Elements": axioms
Archimede

the decimal place-value system
0 and infinity
pi
Brahmagupta
negative numbers
unknowns in equations
trigonometry
Al-Khwarizmi
algebra
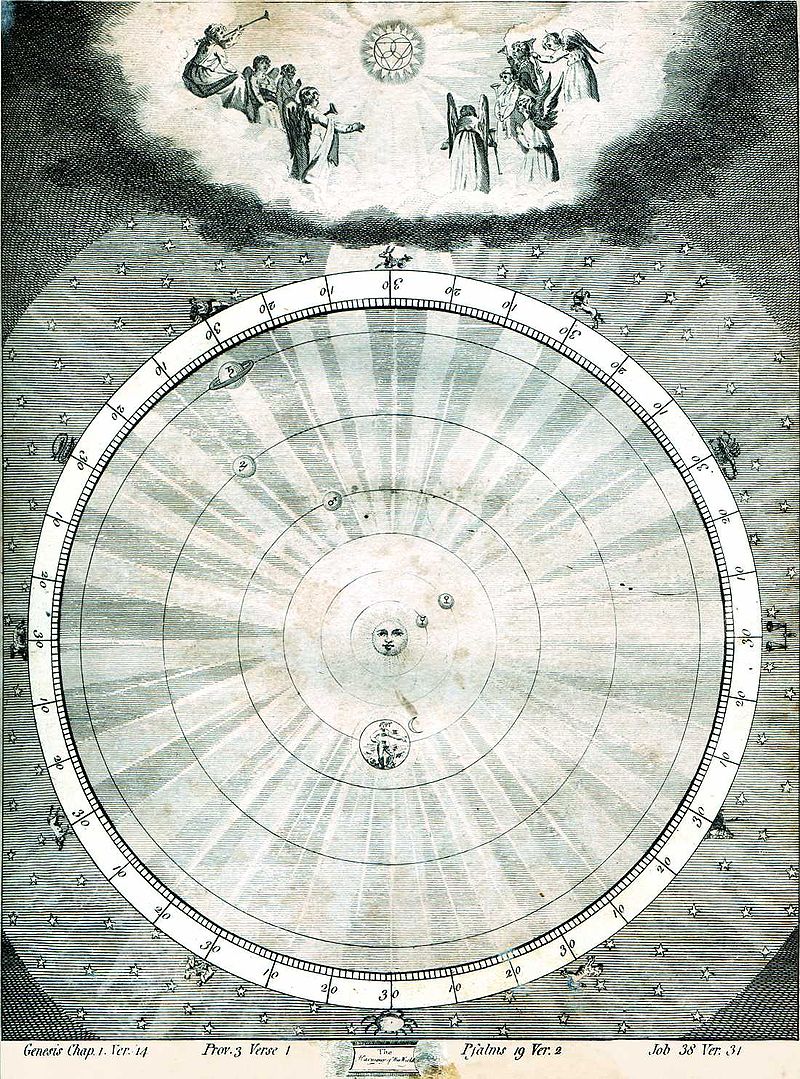
Pythagoras Musica Universalis
Rhythms and intuitive counting
Musical notation and polyphony
12-Tone music and Arnold Schönberg
Stochastic music and Iannis Xenakis
Algorithms and generative music

Crosslink between phonology, music and mathematical description
Semantics and symbol manipulation
logics and reasoning
Mediator of mathematics
Vectorization of language
.svg.png)
Vectorization, stochastic and noise
IQ test
Turing test
Q+ model?
Non-computational problems
